Pneumonia
Written by: Dr. Sabrina Lee
Edited by: Dr. Joann Hsu
The case
17 yo female with no pmhx, UTD vaccines initially in ED for fever (Tmax 101F), productive cough, diarrhea, body aches x 1 week. Testing showed (+) strep and RLL pneumonia. RPP was negative. D/c with Rx of Amoxicillin.
Patient returned 5 days later due to persistent fever and cough and worsening SOB despite outpatient Amoxicillin. She was taking tylenol and motrin at home.
Physical Exam
BP 121/79, Hr 103, RR 28, T 36.9C, SpO2 86% on RA → 91% on 4L NC
GENERAL: Well-nourished, well-developed, well-hydrated, no distress. Vital signs reviewed.
OROPHARYNX: Moist mucus membranes. No erythema, no ulcers, no exudate. Neck is supple, no masses.
CARDIOVASCULAR/HEART: Regular rate & rhythm, normal S1/S2, no murmurs, no rubs, no gallops, normal peripheral pulses.
RESPIRATORY/CHEST: Tachypnea, hypoxia. Decreased breath sounds to the right lung, especially to the right lower lobe.
Labs: CRP elevated to 26.30. Procalcitonin within normal limits. CBC, BMP unremarkable. EPOC unremarkable.
RPP: (+) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Imaging:
CXR: Interval increase in right lower lobe consolidation consistent with pneumonia with adjacent probable pleural effusion.
CT Chest: Near complete right lower lobe consolidation and mild patchy right upper and middle lobe opacities consistent with multifocal pneumonia. Small right pleural effusion.
Bedsde Lung POCUS:
Left lung showed normal lung sliding without B-lines, hepatization, or signs of pleural effusion.
Right lung showed normal lung sliding without B-lines. There was significant hepatization of right lower lobe (more on this later) consistent with pneumonia. Some static air bronchograms noted. Spine sign was seen consistent with pleural effusion.
Characteristics of Pneumonia on Ultrasound:
B-lines - especially focal B lines
Subpleural Consolidations (C-lines)
Pleural Thickening
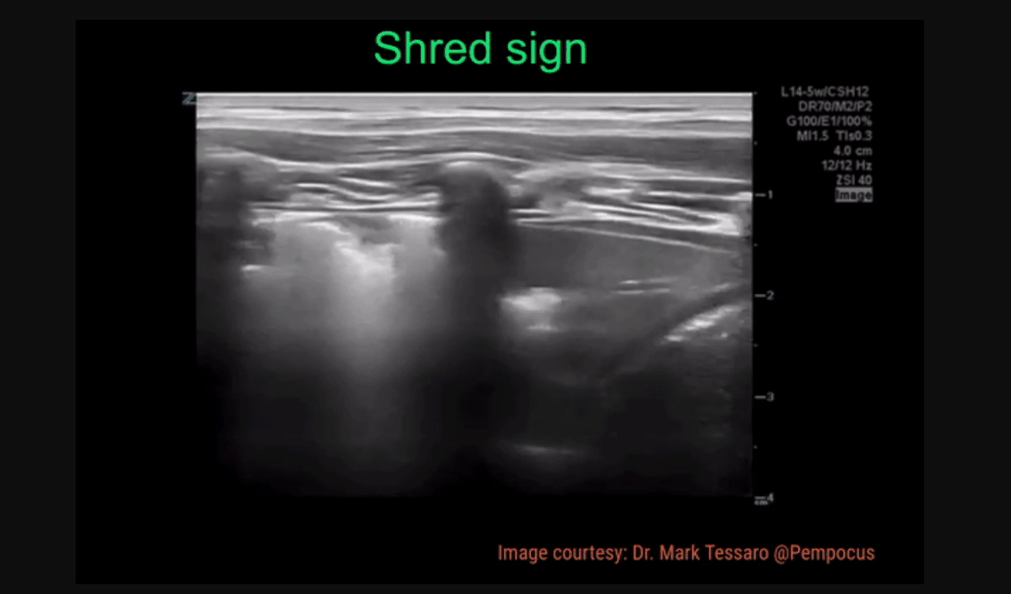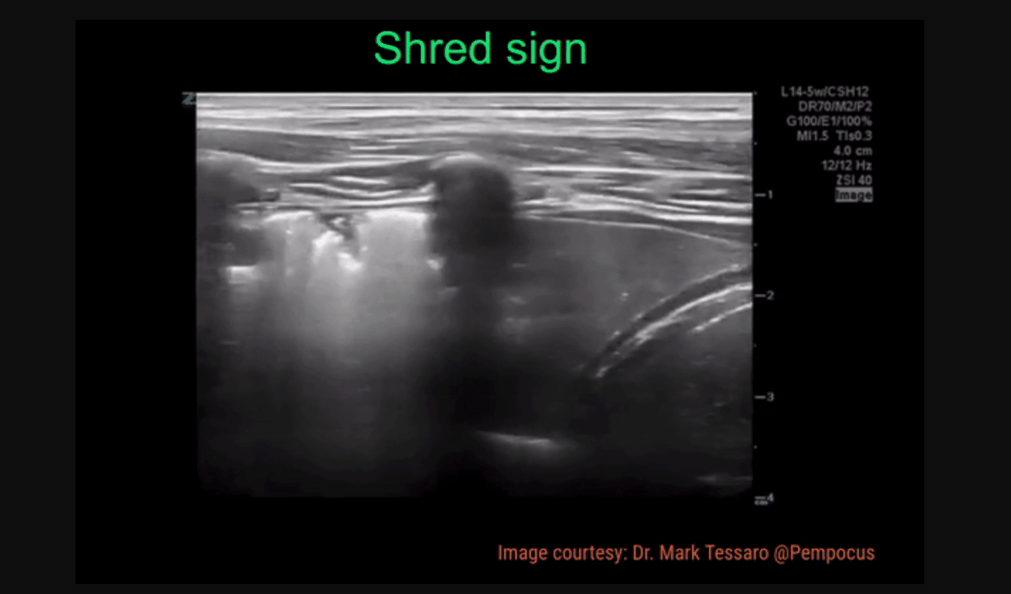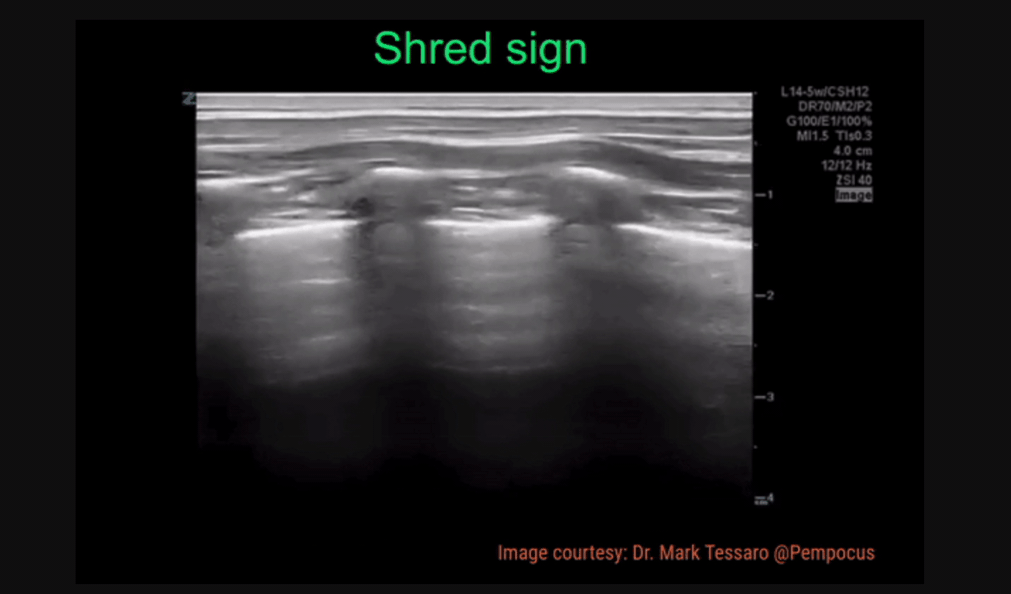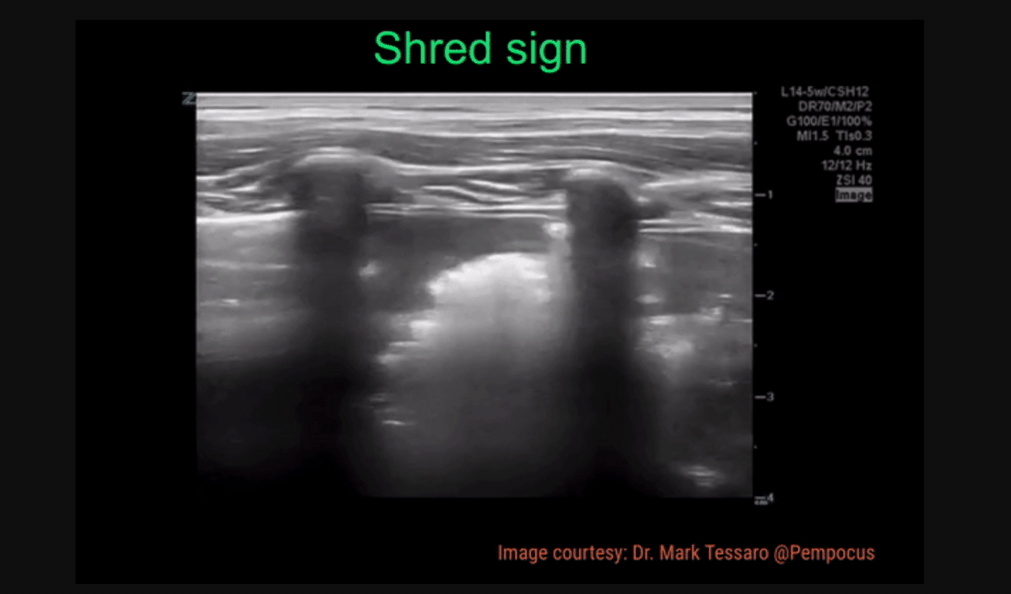
Shred Sign - irregularity of the pleura, looks “shredded”
Hepatization - where the lung looks like liver!
Air Bronchograms
B-Lines: hyperechoic vertical rays from pleural line; localized patches suggest early pneumonia
Subpleural Consolidation (C-lines): cone or dome-shaped consolidations along pleural line; suggests early pneumonia
Pleural Thickening
Shred Sign: irregularity in pleural line, indicating the order between normal aerated lung and fluid/pus-filled lung
Hepatization: dense-appearing consolidation of the lung; seen when lung is completely fluid/pus-filled (pneumonia) or completely collapsed (atelectasis)
Air Bronchograms: small hyperechoic blebs indicated trapped air
Dynamic: movement of air with respiration (as seen in pneumonia) - see first clip
Static: no movement of air with respiration; indicates air is trapped by an obstruction (as seen in atelectasis) - see second clip
Ultrasound Features of Pneumonia by Pathogen:
Lung Abscess
Pus-filled cavity within lung tissue
Commonly caused by aspiration
Common pathogen: Staph aureus
Symptoms:
Fever
Cough
Sweats
Weight loss
Lung Empyema
Pus collection within pleural space
Common pathogen: Staph aureus
Symptoms:
Fever
Chest pain
Cough
Sweats
Weight loss
Which is better - chest XR or US?
Study #1:
A systemic review of multiple studies examining the sensitivity, specificity, and overall accurate of lung US compared to CXR in diagnosing pneumonia
Conclusion; US is generally more sensitive and specific over CXR in multiple studies
Lung US is effective and advantageous across all age groups (pediatric, geriatric, adults)
Study #2:
A prospective, observational study that examined sensitivity and specificity of lung US and CXR in diagnosing pneumonia in a resource-limited setting, specifically Nepal
Conclusion: LUS had better sensitivity than CXR to diagnose PNA in Nepal
Sensitivity: LUS 91% vs CXR 73%
Specificity: LUS 61% vs CXR 50%
Study #3:
A single-center, prospective, observational study that examined the sensitivity and specificity of lung US and CXR in diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia at an urban university
Conclusion: LUS had better sensitivity than CXR to diagnose COVID-19 PNA
Sensitivity: LUS 97.6% vs CXR 69.9%
Specificity: LUS 33.3% vs CXR 44.4%
Benefits to Lung US
Cost-effective
Portable (at bedside)
Safety (less radiation)
Quicker to perform than CXR
More sensitive at diagnosing pneumonia than CXR
Limitations to Lung US
Operator dependent
Patient limitations (habitus, subcutaneous emphysema, large thoracic dressings)
Unable to detect hyper-inflated lung fields from increased intrathoracic pressures
Requires extra time by operator
Can miss lesions that do not extend to pleura (similar to CXR)
Back to our patient…
ED:
Patient required 5L NC and desatted to high 80s on RA
CT surgery consulted for possible chest tube placement but deemed not necessary at the time and to admit
Treated with 1L NS fluids and IV levofloxacin
Admitted to pediatric floors
Floors:
Hospitalized for 4 days
Completed 5-day course Azithromycin and 3-day course Unasyn
Discharged with Azithromycin & Augmentin
Happy scanning!
References
Abid I, Qureshi N, Lategan N, Williams S, Shahid S. Point-of-care lung ultrasound in detecting pneumonia: A systematic review: Published in Canadian Journal of Respiratory therapy. Canadian Journal of Respiratory Therapy. January 29, 2024. Accessed January 26, 2025. https://cjrt.ca/article/92182-point-of-care-lung-ultrasound-in-detecting-pneumonia-a-systematic-review.
Amatya Y, Rupp J, Russell FM, Saunders J, Bales B, House DR. Diagnostic use of lung ultrasound compared to chest radiograph for suspected pneumonia in a resource-limited setting. Int J Emerg Med. 2018;11(1):8. Published 2018 Mar 12. doi:10.1186/s12245-018-0170-2
Boccatonda A, Cocco G, D’Ardes D, et al. Infectious pneumonia and lung ultrasound: A Review. Journal of clinical medicine. February 10, 2023. Accessed January 26, 2025. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9964129/.
Gibbons RC, Magee M, Goett H, et al. Lung Ultrasound vs. Chest X-Ray Study for the Radiographic Diagnosis of COVID-19 Pneumonia in a High-Prevalence Population. J Emerg Med. 2021;60(5):615-625. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2021.01.041
Koratala A, says: jose de jesus C, says: AK. Pneumonia and Dynamic Air Bronchograms. NephroPOCUS. May 22, 2020. Accessed January 26, 2025. https://nephropocus.com/2019/07/01/dynamic-air-bronchograms-ultrasound-sign-of-pneumonia/.
Lung. MMHEME. Accessed January 26, 2025. https://www.mmheme.org/lung.
Rippey J. Lung ultrasound: Pneumonia. Life in the Fast Lane • LITFL. August 23, 2022. Accessed January 26, 2025.
Ultrasound diagnosis of pneumonia. Emory University Shield. Accessed January 26, 2025. https://med.emory.edu/departments/emergency-medicine/sections/ultrasound/case-of-the-month/lung/pneumonia.html.